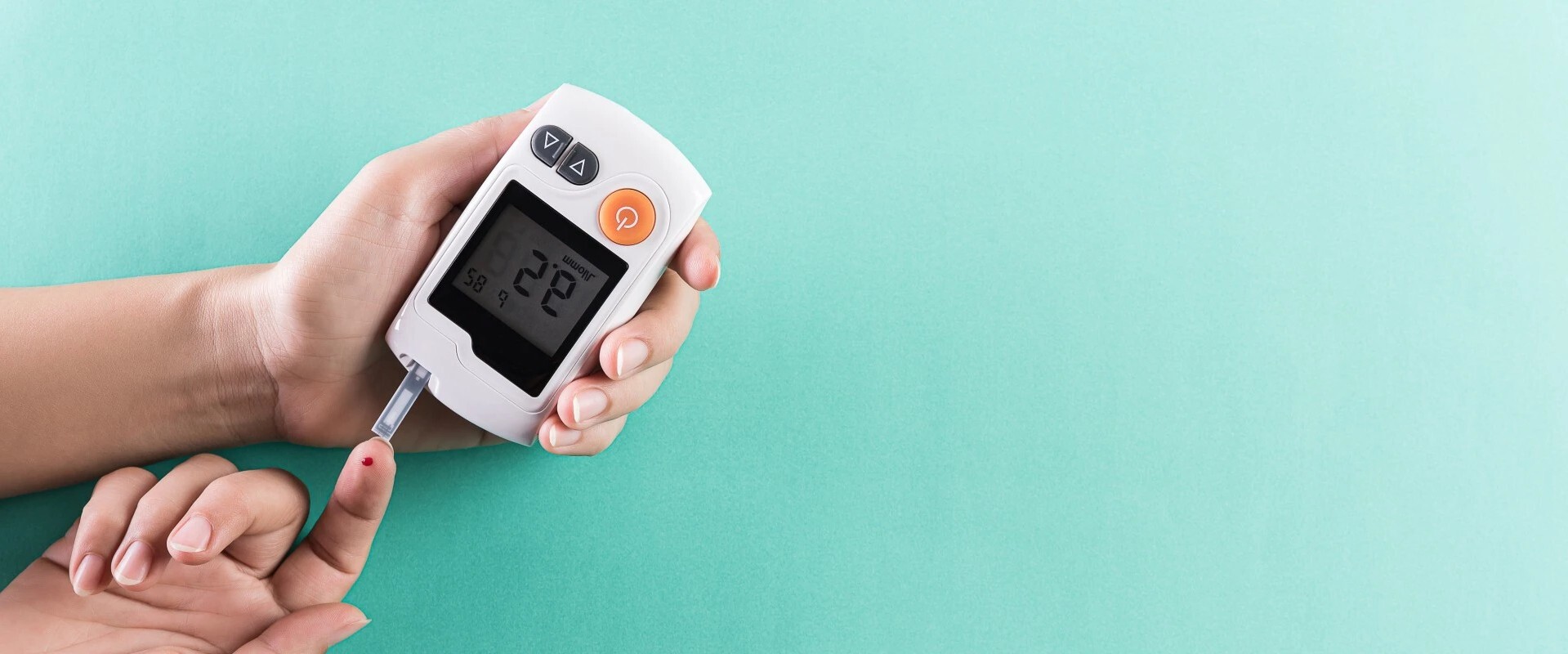
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Stem Cells For Diabetes
- Regeneration of Insulin-Producing Cells: MSC therapy can potentially regenerate pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production, helping to restore insulin levels in Type 1 diabetes.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: In Type 2 diabetes, MSCs may enhance insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively and better regulate blood sugar levels.
- Immune System Modulation: MSCs can modulate the immune system, potentially preventing further autoimmune attacks on beta cells in Type 1 diabetes and reducing inflammation associated with both types.
- Reduction of Chronic Inflammation: MSC therapy has anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce the chronic inflammation that contributes to insulin resistance and complications in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: MSCs can promote tissue regeneration, improving the function of damaged organs, including the pancreas, which helps support overall metabolic health.
- Enhancement of Vascular Health: MSC therapy can stimulate the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), improve circulation, and reduce the risk of vascular complications common in diabetes, such as diabetic neuropathy.
- Potential for Long-Term Blood Sugar Control: By addressing the underlying causes of diabetes, MSC therapy holds the potential for sustained blood sugar regulation, potentially reducing the need for insulin or other medications.
The Most Advance Treatments Available
Stem cell therapy has helped many by promoting healing, reducing inflammation, and regenerating tissue. Patients with autoimmune diseases, injuries, and neurodevelopmental disorders report improved mobility, less pain, and better cognitive function. While research continues, it offers hope for innovative treatments.
Citations & Scientific References
View our medical studies and published studies that support the science behind stem cell therapy.
Clinical StudiesDiabetes Type 1
- Stem cell therapy for insulin-dependent diabetes: Are we still on the road? Lu Yang, Zhu-Meng Hu, Fang-Xu Jiang, Wei Wang – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9350623/
- Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation therapy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Yanju Li, Feiqing Wang, Huiling Liang, Dongxin Tang, Mei Huang, Jianing Zhao, Xu Yang, Yanqing Liu, Liping Shu, Jishi Wang, Zhixu He & Yang Liu – https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-021-02342-5
- Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in treating both types of diabetes mellitus and associated diseases. Vidul Goenka, Tanhai Borkar, Aska Desai & Raunak Kumar Das – https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40200-020-00647-5
Diabetes Type 2
- Evaluating the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Yu Li, Guangren Yue, Shuying Yu, Xinhao Cheng, Yilin Cao, Ximei Wang – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/bioengineering-and-biotechnology/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2024.1349050/full
- Advancing diabetes treatment: the role of mesenchymal stem cells in islet transplantation. Lisha Mou, Tony Bowei Wang, Xinyu Wang, Zuhui Pu – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389134/full
- Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: a single-center, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial. Li Zang, Yijun Li, Haojie Hao, Jiejie Liu, Yu Cheng, Bing Li, Yaqi Yin, Qian Zhang, Fei Gao, Haibin Wang, Shi Gu, Jia Li, Fengxiang Lin, Yingfei Zhu, Guanglei Tian, Yulong Chen, Weijun Gu, Jin Du, Kang Chen, Qinghua Guo, Guoqing Yang, Yu Pei, Wenhua Yan, Xianling Wang, Junhua Meng, Saichun Zhang, Jianming Ba, Zhaohui Lyu, Jingtao Dou, Weidong Han & Yiming Mu – https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-022-02848-6
- Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in treating both types of diabetes mellitus and associated diseases. Vidul Goenka, Tanhai Borkar, Aska Desai & Raunak Kumar Das – https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40200-020-00647-5
Other Autoimmune Diseases Therapies
Hear What Our Clients have to say!
Averaging 5 Stars across multiple platforms — TOP RATED
The Process
Day 1: US ➜ Mexico
- Receive the procedure at the clinic.
- Go back to the hotel and rest (you can stay in a Tijuana hotel or hotel in San Diego).
Day 2: Travel back home
- Check out of your hotel.
- Meet your driver outside the hotel for a smooth ride to San Diego International Airport.
- Arrive at the airport in time to catch your flight back home.
Stem Cells For Diabetes FAQ's
You have questions, we have answers.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune response where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is primarily due to insulin resistance, where the body does not respond effectively to insulin, often combined with insufficient insulin production.
Common symptoms of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores. Type 1 diabetes may also present with sudden weight loss and nausea. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually and may include symptoms like increased hunger and numbness in the hands or feet.
Type 1 diabetes is primarily treated with insulin therapy, either through injections or an insulin pump, along with blood sugar monitoring. Type 2 diabetes is managed through lifestyle changes like diet and exercise, oral medications, and sometimes insulin, depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, newer treatments like GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors may also be used.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be crucial in treating diabetes mellitus by promoting the regeneration of insulin-producing beta cells, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing inflammation. Their regenerative and immune-modulating properties hold potential for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes management.
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy shows promise for treating both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Still, its suitability depends on individual factors such as the severity of the condition, overall health, and specific treatment goals. Clinical evaluations are necessary to determine if MSC therapy is appropriate for a patient.
While mesenchymal stem cell therapy may improve insulin production and sensitivity, any changes to diabetes medication should only be made under a doctor’s supervision. Gradual reduction or discontinuation of medication may be possible, but it depends on individual progress and response to therapy.